Circuit diagrams are graphical representations of how electric current flows within a circuit. Whether used in GCSE Physics or for engineering, electronics, and other related scientific activities, understanding how to interpret and create circuit diagrams is fundamental.
When first learning about circuit diagrams young people often find themselves overwhelmed by the number of lines and symbols used. Despite this intimidating first impression, once you get to grips with what a few of the main symbols mean, you realise how straightforward the diagrams can be.
The most fundamental concept behind circuit diagrams is that particular components, such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors, each have their own distinct symbol which reflects their function in the system. By learning to identify these components, plus basic ones like batteries and switches, it will become much easier to understand the circuit as a whole.
Using colored pens to annotate diagrams can help to make them easier to read. By separating out the different elements of the circuit’s circuitry, you can more easily keep track of the flow of electricity and make sense out of any written instructions. Even if a circuit diagram is too complicated for you to make out alone, simply adding some color to it can break down the process into more manageable chunks.
Circuit diagrams can also be used to construct physical models. This allows students to ‘see’ how the components interact and the changes that occur within the circuit as it operates. This hands-on experience can be invaluable for really getting to grips with the underlying principles involved.
Overall, learning about circuit diagrams is an excellent way for young people to develop an understanding of electricity and how it powers our world. For those studying GCSE Physics, the basics of circuit diagrams are essential, as they will form the foundation for gaining knowledge and understanding of all aspects of electricity and energy.

Gcse Physics Electricity What Is The Resistance Of A Parallel Circuit How Can Total Be Calculated Science

Gcse Physics How Does A Circuit Breaker Work What Is An Mcb Electromagnetism Science

Energy And Voltage In Circuits The Science Hive

Series And Parallel Circuits Physics Gcse Revision
Swot Revision

Circuits What Series Vs Parallel Measuring Cur Voltage

Series And Parallel Circuits Physics Gcse Revision

Energy And Voltage In Circuits The Science Hive

Electrical Circuit Symbols Gcse Physics Revision

Ks4 Electric Circuits Sutton Grammar School

Gcse Physics How Does A Relay Work Why Is Electromagnetism Science

Gcse Physics Electromagnetism How Does A Residual Cur Circuit Breaker Work Rccb Science
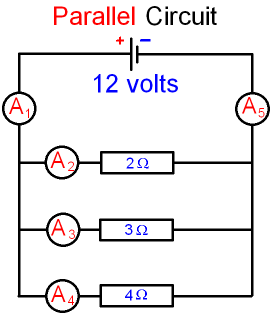
Gcse Physics Electricity What Is The Cur In A Parallel Circuit How To Calculate Science
Exampro Gcse Physics

Physics 1 Electrical Circuits Flowchart

Aqa Gcse Physics 4 1 Electric Circuits Diagram Quizlet
